Interesting Facts
Do you know:

Timing is certainly critical!
Measures of brain activity show that during the second half of a child's first year to the first decade of life, the prefrontal cortex, the seat of forethought and logic, develops synapses at a furious rate that it consumes twice as much energy as an adult brain.
“Use it or Lose it"
Lacking appropriate brain stimulations during the development years has a significant negative impact on the cognitive ability of children and correlates with decline in brain performance later in life.
Math Anxiety
Do you know:

Using a calculator might restrict the level of expertise achieved with respect to short-term memory skills for complex arithmetic." Complex arithmetic places special demands on short-term memory skills that simple arithmetic usually does not, because complex arithmetic involves operations such as carrying, borrowing and place keeping. "This is demanding mental juggling for most people's short-term working memory processes.
Math anxiety worsens performance in two ways: First, it leads to avoidance, which leads to lower competence; second, it temporarily inhibits working memory capacity, possibility by failure to inhibit attention to intrusive thoughts.
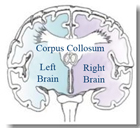
80% of the world's people have a more developed left brain.
Dr. Roger Sperry of the California Institute of Technology won a Nobel Prize for his work on the functions of the brain's hemispheres.
The right brain has a "high speed, high capacity memory" mechanism.
Neural Pathway
Our brain cells (call Neurons) communicate with each other through an electrochemical network of connections call synapses. The information go into a neuron's body through a thin extension call dendrites (see above picture) and the thicker extension call axons take information away from the cell body.
Understanding Our Brain
Abnormalities in the production or functioning of certain neurotransmitters have been implicated in a number of diseases including Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and clinical depression.
The human brain consists of some 100 billion interconnected nerve cells with innumerable extensions.
Using EEGs to enhance biofeedback, a person can be taught to monitor and regulate his or her own brain waves.
In the 1970s psychologist M. Barry Sterman taught cats to control their brainwaves in his laboratory.
Brainwave training is an effective intervention for epileptic seizures in humans.
One hundred billion neurons may seem like a lot of nerve cells, but is actually only about 20% of the number we originally start with....
Chronology
1929: Hans Berger, wiring up his son, discovered that the brain generates different electrical frequencies and called the resulting chart "Electroencephalogram" (EEG).
1930: Ivan Petrovich conducted the famous experiments on his dogs. The concept of conditioning is born.
1950: Neal E. Miller of Yale University proved that control of automatic functions (e.g. heart rate) can be taught.
1967: M. Barry Sterman taught his cats to control their brain wave and the resulting subject becomes resistant to epileptic seizures.
1970: Joel Lubar proved that brain wave pattern correction is effective for attention deficit disorder (ADD) and hyperactivity.
1993: University of Vienna researchers Jakob Pietschnig, Martin Voracek and Anton K. Formann presented quite definite findings that suggest no evidence for specific cognitive enhancements through mere listening to Mozart music. Emory University psychologist Scott E. Lilienfeld, who in his recent book "50 Great Myths of Popular Psychology" has already ranked the "Mozart effect" number six.
1998: New York school district incorporated EEG biofeedback into its educational system to treat learning disabilities and hyperactivity.
Four State of the Brain
Types Of Brain Waves:
BETA: The most rapid is called a beta brain wave pattern, the pattern of normal waking consciousness. Beta is associated with concentration, arousal, alertness, and cognition. At its highest, most rapid levels, though, beta is associated with anxiety, disharmony, and unease.
ALPHA: Relaxed, brain wave activity slows into what is called an alpha brain wave pattern. Alpha patterns vary from deep alpha, a state of deep relaxation often referred to as the "twilight state" between sleep and waking, to the higher end of alpha which is a more focused yet still very relaxed state. Thus it is also referred to as the 'super-learning' state.
THETA: Slower still are theta waves. Theta is best known as the brain wave state of dreaming sleep, but it is also associated with a number of other beneficial states, including increased creativity, some kinds of "super learning," increased memory abilities, and what are called integrative experiences. "Ah-ha!" experiences, where you suddenly "get it," have an insight, are accompanied by bursts of theta waves in your brain.
DELTA: The slowest brain wave pattern is delta, the brain wave pattern of dreamless sleep.
Interesting News
Mathematical knowledge of half a million students from forty-one countries was tested. Of these countries, the test shows that American students performed below average in mathematics. One of the most famous studies of its kind is called Pursuing Excellence, the Third International Mathematics and Science Study.
The mathematical education provided in the United States has proved to be inferior compared to that of other countries. Specifically the Japanese and other Asian educational systems produce more educated mathematics students than the United States. American children tend to score lower on standardized testing than Asian students do.
Many studies have been done by research groups such as the National Center for Education Statistics of the U.S. Department of Education and the International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement showing the differences in teaching methods between the United States and Japan.
Do you know:
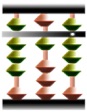
A traditional abacus has 2 fives and 5 ones on each column because of 16 based calculation of old Chinese unit of measurement.
A modern abacus has 1 five and 4 ones on each column because of 10 based calculation.